Nutrition
Most of the major world dietetic associations and many health organisations, including the British NHS, the American Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, agree that a 100% plant based diet fulfills all our nutritional needs, at all stages of life. In fact, one of the benefits of being an ethical vegan is the happy co-incidence that a plant based diet can help prevent many illnesses that cause suffering and premature death in the Western World.

“With good planning and an understanding of what makes up a healthy, balanced vegan diet, you can get all the nutrients your body needs.” (NHS).
“It is the position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics that appropriately planned vegetarian, including vegan, diets are healthful, nutritionally adequate and may provide health benefits for the prevention and treatment of certain diseases. These diets are appropriate for all stages of the life cycle, including pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, adolescence, older adulthood and for athletes. Plant-based diets are more environmentally sustainable than diets rich in animal products because they use fewer natural resources and are associated with much less environmental damage. Vegetarians and vegans are at reduced risk of certain health conditions, including ischemic heart disease, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, certain types of cancer, and obesity. Low intake of saturated fat and high intakes of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, soy products, nuts, and seeds (all rich in fiber and phytochemicals) are characteristics of vegetarian and vegan diets that produce lower total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and better serum glucose control. These factors contribute to reduction of chronic disease. Vegans need reliable sources of vitamin B-12, such as fortified foods or supplements.” (Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 2016;116:1970-1980.)
Progress is being made around the world in collaborative efforts between health, environmental and ethical specialists to promote plant diets as the solution to many interrelated world problems.
It is important to be responsible for your health. Becoming vegan does not guarantee good health or immortality. Vegans get sick and they die, just as non-vegans do. Eating a junk food plant based diet will not do your health any favours. However, with a little planning and experimentation with new recipes, you can easily eat a delicious diet that is not only part of an ethical lifestyle, but also has many health benefits.

The key to a healthy diet is good planning. This is not unique to a plant based diet. Familiarise yourself with nutritional guidelines to ensure that you are eating in such a way that you get sufficient energy, protein, iron, Vitamin B12, Vitamin D2, iodine, and calcium. There are excellent sources of reliable information on the internet. Some of them are mentioned in the resources section of this website. Do not underestimate the value of consuming fortified foods. Food fortification is the practice of adding essential vitamins and minerals (e.g. iron, vitamin A, folic acid, iodine) to staple foods to improve their nutritional content. In an omnivorous world fortification is regarded as a a safe, effective way to improve public health that has been used around the world since the 1920s. In a vegan world, staple foods will simply be fortified with the nutrients that are of specific relevance to those who only eat plants: calcium, selenium, zinc, iodine, Vitamin B12, Vitamin K, Vitamin D and possibly Omega 3 Fatty Acids.
If you need extra assurance about how a diet of plants can meet your nutritional requirements buy one of the recommended books on Vegan Dietetics & Plant Nutrition; join a vegan education class, or consult a Plant Based Registered Dietitian or nutritionist.
Download The International Vegan Association Leaflet Demystifying Vegan Nutrition
There are some nutritionists who can advise on Plant Based Nutrition.
Sandra Hood is a Registered Dietitian, BDA Member and BDA Public Health Nutrition Specialist Group Committee Member. She specialises in Plant Nutrition for Parents and Children.
There is now a very rich source of information in the UK from Plant Based Health Professionals UK.
If you have health concerns you can also consult your General Practitioner but it is advisable to also consult someone who has expertise in plant nutrition.
There is an excellent Meal Planner in the 21 Day Vegan Kickstart available from Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. Although there may be some cultural differences between American and European food and diet, you can easily adapt it to suit your lifestyle. (Please note that all references to ‘vegetarian’ diets on this website mean 100% vegan plant diets.)
Key Components of a Healthy Plant Diet
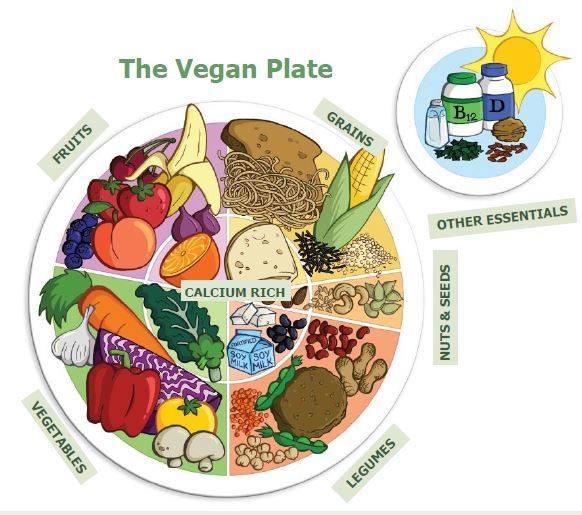
Daily Recommendations
For more detailed information on daily recommendations, consult one of the books in the resources section below.
Protein: Protein sources include legumes, nuts, seeds, and grains. Soy products, such as Tofu, Seitan and Tempeh, as well as meat analogues, are useful sources of protein.
Vitamin B12: is not found in plant foods. However, that is not a justification for eating animals. Neither plants nor animals synthesize this vitamin. It is made by bacteria. B12 is a very important nutrient and deficiency can have detrimental effects on our health. A reliable source of Vitamin B12 is recommended for everyone over the age of 50, including those who are not vegan. Some studies show that a significant percentage of the general population (39%) have insufficient B12 levels (Tucker et al, 2000: American Society for Clinical Nutrition). So it is not only something vegans need to be aware of.
Further information is available on the following pages:
There are some excellent books, documentaries and website resources that can help your understanding and guide your practical application of veganism to the food you eat. Here are some of them:
Books
- Becoming Vegan: The Complete Guide to Adopting a Healthy Diet, Brenda Davis & Mesanto Melina
- Vegan for Life: Everything You Need to Know to Be Healthy and Fit on a Plant-Based Diet
Medical Doctors supporting a Vegan Diet
- Michael Klaper, MD
- Michael Greger, MD
- Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (particularly strong on preventing and treating Type II Diabetes with diet)
- Plant Based Health Professionals UK
Films & Documentaries